| Virt-Manager |
 |
 |
 |
|
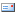
Virtual Manager is a desktop user interface for managing virtual machines. In order to be managed within virt-manager, virtual machines must be imported in the the xenstore, so that libvirt library can recognize and manage them, via the command: root@serv1:~# xm new /etc/xen/vm.cfg (syntax: xm new ) Every time .cfg is modified, the virtual machine(s) to be imported must be deleted from xenstore root@serv1:~# xm delete vm and then added back to it again. Once inserted in the xenstore, virtual machines can be shown through the command: root@serv1:~# xm list even if the are not booted (normally, this would not be true). In order to start/stop them from command line, the command: xm create /etc/xen/vm.cfg (or xm shutdown vm) does not work anymore. The command: root@serv1:~# virsh start vm (and virsh shutdown vm) must be used instead. After having done so for every virtual machine we intend to manage, two management modes are possible: 1) local (on xen Dom0) Only in this mode, the function “create new virtaul machine” is active. So: root@serv1:~# aptitude install virt-manager (add "sudo") 1.a launching from graphical interface (insert user password for sudo) 1.b launching from command line by connecting via ssh, with X forwarding enabled, in the following way: user@yourpc:~$ ssh user@serv1 -X -C (instert user password for sudo) 2) remote (from a client) (xend-http-server yes) (xend-unix-server yes) Then, in the client: root@yourpc:# aptitude install virt-manager and then launch virt-manager from menu "application" -> "system tools" (under gnome). |

